Study Guide
Field 014: Earth and Space Science
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
Competency 0001
Understand principles and processes of scientific inquiry.
A researcher collects water samples from a pond. The dissolved oxygen content of the samples will be measured later in a laboratory to determine the dissolved oxygen content of the pond's water. Which of the following procedural steps taken by the researcher will help ensure that the samples accurately reflect the dissolved oxygen content of the pond water?
- collecting samples from the surface in the same near-shore location and keeping the sample jars cool until testing is done
- filling sample jars to the top with water collected from several recorded depths and locations and then rapidly sealing them for storage
- allowing the samples to sit open for a period of time to equilibrate with atmospheric conditions and then sealing them until they are tested
- mixing the samples together to minimize differences that may result from human error and from the variability of the samples
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to apply methods and criteria for collecting scientific data. In this case, the examinee is required to evaluate proper collection procedures for water samples that will be collected from a pond. The water samples are to be analyzed later in a laboratory for dissolved oxygen content. The dissolved oxygen content of samples can change when the water is exposed to the atmosphere, so the sample containers should be filled to the top and rapidly sealed. Since the dissolved oxygen content of pond water can vary at different locations and depths, it is important that the sampling include several locations and that these details be recorded on the containers.
Competency 0002
Understand the history and nature of science.
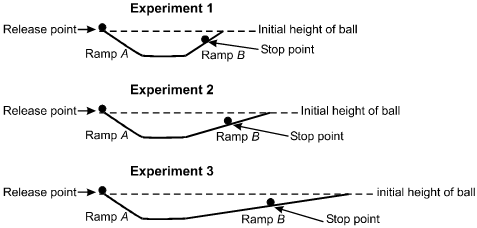
A researcher conducts three experiments as shown in the diagram above. In each experiment, a ball is released at the top of Ramp A. The researcher observes the ball as it rolls down Ramp A, across a flat surface, and up Ramp B, where it eventually stops and then rolls back toward Ramp A. The researcher predicts that if Ramp B was actually flat and friction did not slow the ball, the ball would roll forever. This series of experiments most closely resembles experiments conducted by:
- Archimedes as he developed his law of buoyant force.
- Kepler to explain the character of planetary motions.
- Galileo as he developed the concept of inertia.
- Newton as he developed his third law explaining action-reaction pairs.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the principle of inertia developed by Galileo and the inclined plane experiments associated with that work. In his writings, Galileo noted that a ball rolling down an inclined plane and then up a second inclined plane seeks to retain its original height, regardless of the angle of the second incline. From this observation, Galileo speculated that if the second inclined plane were instead a flat, frictionless plane, the ball would continue rolling at the velocity it had attained during its descent. Galileo's idea that an object resists change to its state of motion unless acted on by a force provided the basis for Isaac Newton's law of inertia.
Competency 0003
Understand the relationships between science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Which of the following technologies has been most widely used to locate offshore petroleum resources?
- sonar
- seismic wave reflection
- magnetometry
- ground-penetrating radar
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to analyze the interrelationship between a technology used in offshore petroleum prospecting and the laws of physics. Prospecting for petroleum resources with seismic reflection takes advantage of the differential reflection of seismic waves as they encounter different layers of material beneath the ocean floor. Sensitive instruments towed behind a boat and located below the water surface record the time it takes for the various reflected seismic waves to arrive at the recording devices. A series of these measurements can be used to identify different layers and structures beneath the ocean floor, including petroleum traps where petroleum deposits accumulate.
Competency 0004
Understand historical geology.
Which of the following statements describes the scientific basis of radiometric dating?
- The radioactivity of a rock sample is inversely related to the amount of time that has passed since the rock was exposed at Earth's surface.
- The proportion of alpha particles to beta particles given off by radioactive elements in a particular rock is a measure of the rock's age.
- The concentration of different types of radioactive isotopes in a rock indicates the geologic period in which the rock formed.
- The proportion of radioactive parent atoms to daughter atoms in a rock is used to calculate the time that has elapsed since the rock formed.
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the absolute dating of geologic events using the breakdown of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes. This technique, known as radiometric dating, relies on the fact that different radioactive isotopes have different decay rates that are constant under conditions found in Earth's outer layers. As a radioactive isotope decays, it produces decay products, known as daughter products, at a rate specific to that isotope. The proportion of the original radioactive isotope in a rock to the daughter products that have formed over time provides a tool for measuring the time that has elapsed since the rock first formed.
Competency 0005
Understand plate tectonics and the rock cycle.
The upwelling of magma in an active volcano has the greatest potential for producing a dangerous pyroclastic flow if the magma:
- contains a high concentration of dissolved gases and a high silica content.
- is basaltic and contains very little water vapor.
- contains low levels of volatile gases and erupts at a relatively high temperature.
- is andesitic and has a relatively low viscosity.
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of different types of volcanic activity. Pyroclastic flows are associated with explosive eruptions from composite cones. Typically, the magma has a high silica content, making the magma relatively viscous, and a high concentration of dissolved gases. As the magma moves upward, the gases in it are unable to escape from the magma because of its high viscosity. Pressure builds within the volcano toward a sudden explosive eruption. Pyroclastic flows can be triggered by a lateral explosion from a composite volcano or, more commonly, from the collapse of a tall eruption column emitted during a major explosion from the top of the volcano's main vent. Pyroclastic flows consist of a mix of heated gases, incandescent ash, and rock fragments that move rapidly down the slopes of a volcano, often at speeds over 100 miles per hour.
Competency 0006
Understand Earth materials, geologic resources, and Earth's internal structure.
Which of the following physical properties is used to classify minerals in Bowen's reaction series?
- crystallization temperature
- specific gravity
- crystal form
- hardness
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the classification of minerals. Bowen's reaction series is a mineral classification scheme that describes the sequence in which minerals crystallize from a magma as the magma cools. For example, minerals containing iron, magnesium, and calcium crystallize first from the hot magma, depleting the remaining magma of these elements. As the magma cools, the very last minerals to form from the depleted magma are potassium feldspar, muscovite mica, and quartz.
Competency 0007
Understand the processes of weathering, erosion, and deposition.
The formation of karst topography in regions underlain by limestone occurs when:
- calcium carbonate combines with water molecules to form a hydrated compound that is easily dissolved.
- alkaline groundwater saturates and erodes cracks within the bedrock due to a rise in the elevation of the water table.
- carbonic acid in groundwater reacts with calcite, forming calcium bicarbonate, a soluble mineral.
- tectonic uplift exposes marine sediments to physical weathering that breaks up carbonate rocks along bedding planes.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to analyze the process that produces karst topography in regions underlain by limestone deposits. The development of karst topography begins with the chemical weathering of limestone as it reacts with groundwater. The groundwater is slightly acidic because it contains carbonic acid. The carbonic acid in groundwater is produced by the interaction of precipitation with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and in soils. The carbonic acid in groundwater reacts with calcium carbonate (calcite), the primary component of limestone, to produce calcium bicarbonate. Since the calcium bicarbonate is a mineral that is soluble in water, it is carried away in the groundwater. Over geologic time, this chemical weathering process produces the caverns, sinkholes, and caves associated with karst topography.
Competency 0008
Understand the hydrologic cycle and its interaction with other Earth systems.
During which of the following phase changes would the greatest amount of energy per gram of water be released to the environment?
- Water evaporates from a reservoir on a hot and dry day.
- On a cold fall morning, frost forms on a lawn.
- Ice sublimates on a very cold and dry day.
- On an early summer morning, dew forms on a field.
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to analyze the energy changes that occur as water changes phase. Energy must be added to water to vaporize liquid water or melt ice, however energy is given off by water when the processes are reversed. Frost is a particular case in which water vapor is converted to ice without passing through a liquid phase. It is because of this that the formation of frost releases more heat than the phase change from gas to liquid that occurs during the formation of dew.
Competency 0009
Understand the composition, structure, and properties of oceans.
The continental shelf of the East Coast of the United States comprises:
- thin deposits of marine mud overlying the remnants of ancient limestone reefs.
- salt deposits alternating with layers of basalt.
- shifting sandbars overlying the eroded remains of uplifted oceanic crust.
- thick layers of sand, silt, and mud overlying granitic crust.
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the physical structure of the continental shelf. The continental shelf is the submerged, gently sloping section of the continental margin that stretches from the coastline to the beginning of the much steeper continental slope. Abundant sediments, primarily from the erosion of the adjacent continent, can accumulate to a thickness of several kilometers. These sediments typically range from coarser material that is deposited near the coastline to silt and mud that accumulate farther out on the continental shelf.
Competency 0010
Understand the characteristics and properties of freshwater systems.
A mature river system with a gentle grade flowing over coastal plain sediments is likely to have a configuration most similar to which of the following illustrations?
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of river drainage systems. A mature river flowing across a coastal plain composed of sediments will typically develop a meandering pattern due to the gentle slope of the coastal plain, the slow flow velocity of the river, and the nature of the fine-grained sediments through which it carves its channel.
Competency 0011
Understand the structure and properties of the atmosphere.
In the year following the major eruption of the Mount Pinatubo volcano in the Philippines, a drop in mean global temperature was recorded. Which of the following factors was primarily responsible for this drop in global temperature?
- emission of sulfuric gases from the volcano into the lower stratosphere
- above-average precipitation in tropical regions
- ejection of particulates into the lower troposphere by the volcano
- increased levels of smog-forming nitrogen oxides in the troposphere
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the effects of major volcanic eruptions on the climate system. The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines provided an opportunity for scientists to evaluate the effects of a major eruption on climate. The eruption introduced over 25 million tons of sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere. The oxidation of the sulfur dioxide emitted by the volcano produced a haze of sulfuric acid droplets that spread throughout the stratosphere, significantly reducing the amount of sunlight reaching Earth's surface. This had the effect of lowering the average temperature of the troposphere by approximately 0.5°C following the eruption, while increasing the temperature of the stratosphere.
Competency 0012
Understand the characteristics of weather systems and the circumstances under which various weather conditions develop.
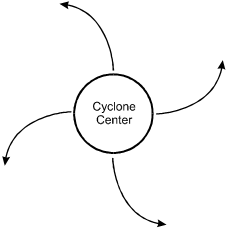
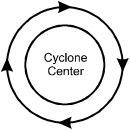
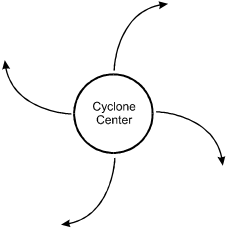
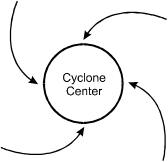
A tropical cyclone in the Gulf of Mexico is moving slowly toward Florida. The flow of prevailing surface winds associated with the cyclone most closely resembles which of the following diagrams?
- Answer
- Correct Response: D. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the wind patterns associated with low-pressure systems in the northern hemisphere. A tropical cyclone is a large low-pressure system that rotates counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere due to the Coriolis effect, producing converging surface winds that pull in air from the surrounding region.
Competency 0013
Understand Earth's climate systems and the factors that influence climate.
The once extensive grassland prairies of the upper Midwest typically did not include forests. Which of the following factors was primarily responsible for the absence of forests in this region?
- low annual precipitation
- winter and summer temperature extremes
- thin topsoil
- summer fires and strong winter winds
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the limited rainfall that characterizes grasslands in general and the once extensive grassland prairies of the upper Midwest in particular. Although temperate grasslands have a fire ecology, grasses dominate in these regions primarily because the annual average rainfall is inadequate to sustain a forest ecosystem.
Competency 0014
Understand the characteristics of stars, galaxies, and the universe.
Which of the following physical characteristics of a main-sequence star is the most important factor in determining its luminosity?
- total mass
- size of the corona
- chemical composition
- strength of the magnetic field
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the physical characteristics of stars. The luminosity of a star is a measure of the amount of energy it radiates each second. Based on research conducted during the 1920s, the astrophysicist A.S. Eddington discovered that the luminosity of a main-sequence star is determined by its mass. Eddington's discovery is the basis of the mass-luminosity relationship L = M 3 , where the luminosity of a main-sequence star is equal to the star's mass cubed. Analysis of the energy emitted by a star continues to be an essential tool that astronomers use to deduce stellar properties, including composition, temperature, size, and mass.
Competency 0015
Understand characteristics and components of the solar system.
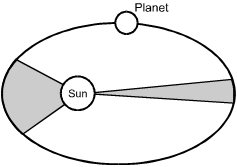
The diagram above shows the distance traveled by a planet at two different intervals in its solar orbit. The astronomer Johannes Kepler compared the two shaded gray areas of the ellipse in order to determine the:
- mass of planets with different orbital periods.
- diameter of the orbits of other planets.
- gravitational pull that the planet exerts on other objects.
- changing speeds at which a planet orbits the sun.
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to recognize the law developed by Johannes Kepler to describe the changing orbital speed of a planet as it travels around the sun. This law states that the orbital speed of a planet varies so that a line joining the sun and the planet will sweep over equal areas in equal time intervals. The graphic in the question represents the two equal areas that a hypothetical planet covers during two different but equal time periods in its elliptical orbit. Since the time periods are the same, but the distance covered during the two intervals is different, the orbital speed must be different.
Competency 0016
Understand the sun-moon-Earth system and the apparent motions of stars and planets.
The large dark areas of the moon known as mares are easily visible from Earth. Which of the following explains the presence of these dark areas?
- Massive volcanic eruptions emptied underlying magma caverns, causing their collapse and the formation of calderas.
- Shortly after the moon's formation, Earth's strong gravitational pull on the moon caused the release of magma from fissures in the crust.
- Large meteorites excavated huge craters that filled with low-viscosity basalt flowing from the fractures created in the underlying crust.
- When the moon was still semi-molten, thin areas of crust collapsed due to tectonic activity, creating low areas that trapped sediments.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the physical characteristics of the moon. The mares on the moon are large dark areas that formed when meteorites slammed into the moon, producing huge craters that then filled with basalt that flowed up into the craters through fractures in the moon's crust.